The Basics:
Rectangles and Squares:
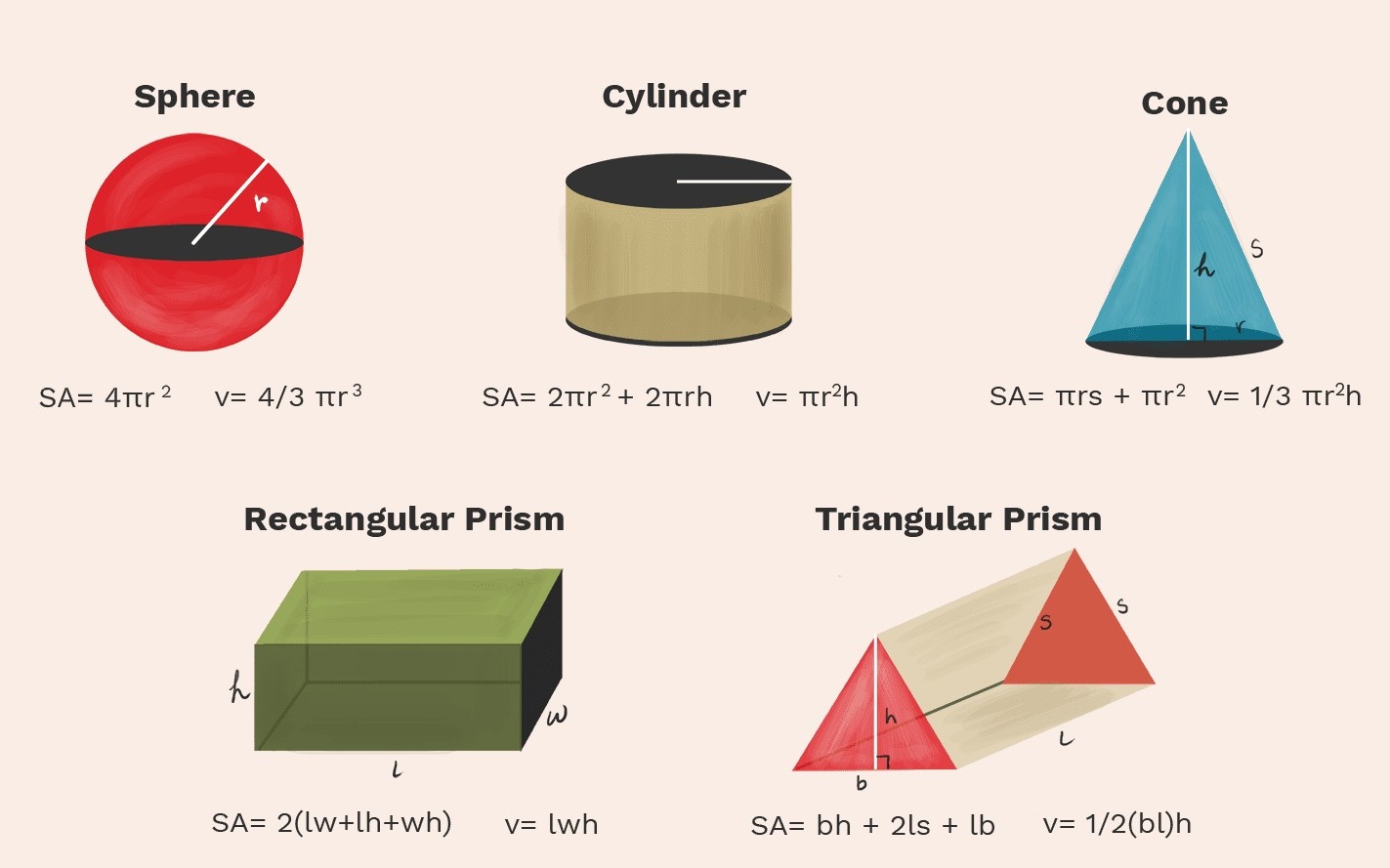
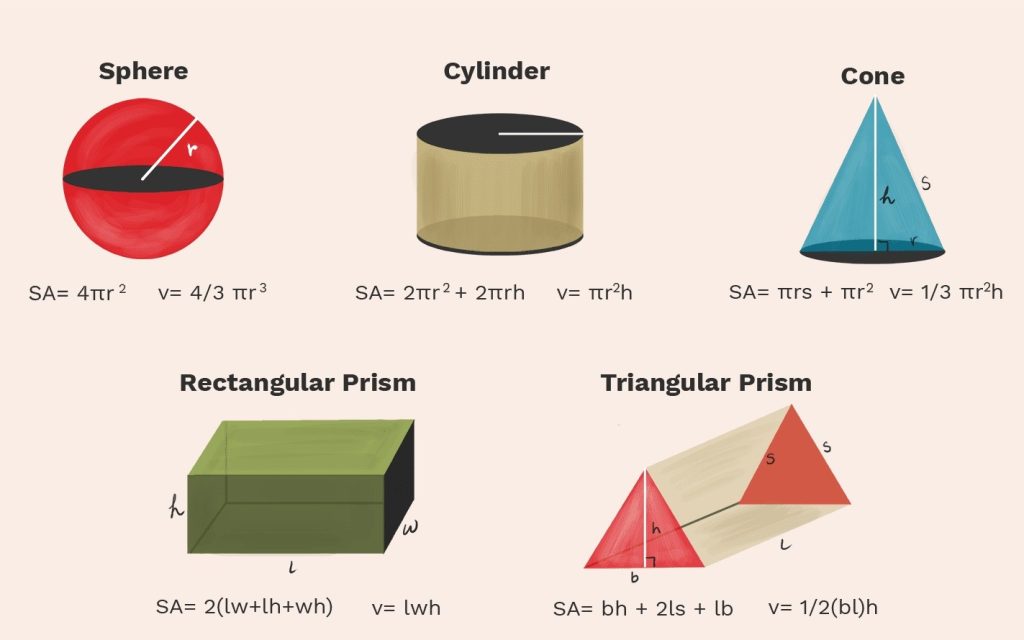
The simplest of them all, the area of a rectangle or square is calculated by multiplying its length and width. Remember, area (A) equals length × width.
Circles:
Enter the realm of curves. For circles, the formula A = πr² involves the radius (r). If you know the diameter (D), you can use the formula A = π(D/2)².
Triangles:
Triangles introduce the concept of halving. To find the area, multiply the base by the height and divide by 2. The formula is A = (base × height) / 2.
Beyond the Basics:
Trapezoids:
These four-sided wonders have a specific formula: A = (1/2) × (a + b) × h, where “a” and “b” are the lengths of the parallel bases, and “h” is the height.
Irregular Polygons:
When dealing with irregular shapes, break them down into simpler components. Calculate the area for each segment individually and sum them up for the total area.
Practical Tips:
Unit Consistency:
Before diving into calculations, ensure all measurements are in the same unit. Consistency is key to accurate results.
Precision Matters:
Precision in measurement is crucial. Round off numbers appropriately to maintain accuracy.
Visualize the Shapes:
Sketching or using graph paper can aid in visualizing shapes and understanding the measurements required for accurate calculations.