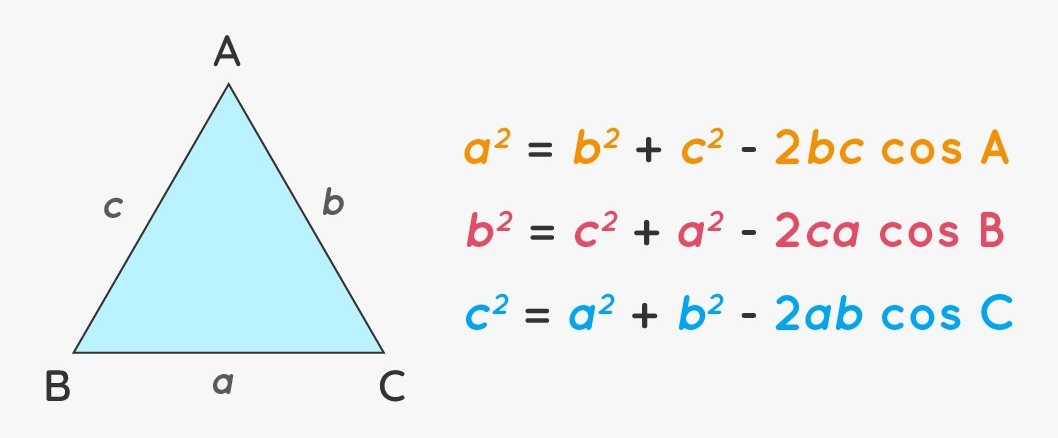Before we dive into the intricacies of sine and cosine laws, let’s refresh our memory on the basics of trigonometry. Trigonometry is the branch of mathematics that deals with the relationships between the angles and sides of triangles. Three fundamental trigonometric ratios—sine (sin), cosine (cos), and tangent (tan)—establish these connections and form the foundation for solving various trigonometric problems.
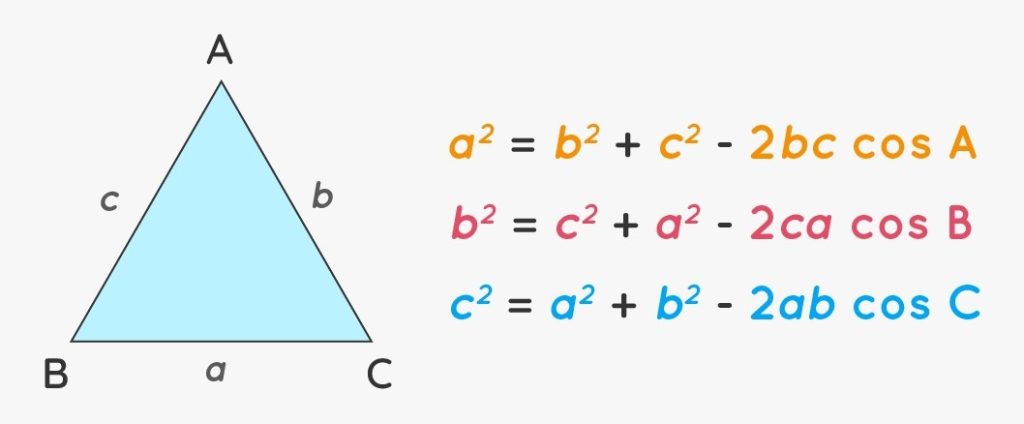
The Sine Law:
Concept:
The sine law, also known as the law of sines, relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the sines of its angles. For any triangle ABC, the sine law is expressed as:
a/sin(A) = b/ sin(B) = c/ sin(C)
where a, b, and c are the sides of the triangle opposite to angles A, B, and C, respectively.
Applications:
The sine law is particularly useful when dealing with triangles that are not right-angled. It empowers students to find unknown sides or angles in triangles with ease, offering a versatile tool for problem-solving in various real-world scenarios.
The Cosine Law:
Concept:
The cosine law, also known as the law of cosines, extends the applicability of trigonometric principles to all types of triangles, whether they are acute, obtuse, or right-angled. For any triangle ABC, the cosine law is expressed as:
c2=a2+b2−2abcos(C)
This law relates the lengths of the sides a, b, and c to the cosine of angle C.
Applications:
The cosine law is invaluable for determining side lengths or angles in triangles when the information about the three sides or two sides and the included angle is available. It’s a powerful tool that transcends the limitations of the sine law in certain scenarios.
Real-World Applications:
Understanding the sine and cosine laws isn’t just about solving abstract mathematical problems. These laws find applications in a multitude of real-world situations. Whether it’s navigating through the great outdoors using trigonometric principles, designing structures, or analyzing data in various scientific fields, the sine and cosine laws prove their relevance time and again.
Tips for Mastery:
- Practice Regularly: Like any skill, mastering trigonometry requires consistent practice. Work on a variety of problems to strengthen your understanding of when and how to apply the sine and cosine laws.
- Visualize Triangles: Use diagrams to visualize the triangles and their respective angles and sides. This helps in developing a clearer understanding of the problems at hand.
- Understand the Context: Relate the mathematical concepts to real-world scenarios. Understanding the context can make the application of sine and cosine laws more intuitive.
- Collaborate and Seek Help: Don’t hesitate to collaborate with peers or seek guidance from teachers. Explaining concepts to others or getting clarification on doubts can significantly enhance your understanding.
– Learn how to solve trigonometry in depth